Treatment of 1,4-Dioxane- and Specialty VOC-Contaminated Water
Emerging contaminants like 1,4-dioxane pose unique remediation challenges. Companies and the environmental engineering consulting firms they hire to remediate sites contaminated by these compounds are often faced with technologies that are unable to achieve consistent results or solutions that are too expensive to maintain. ECT2 has developed a synthetic media treatment system that efficiently and effectively removes 1,4-dioxane and a broad range of other VOCs from Superfund, aerospace, general manufacturing, landfill, and heavy industry sites throughout the United States and abroad. These systems have produced reliably steady, non-detectable effluent concentrations for 1,4-Dioxane and other VOCs commonly encountered in remediation applications.
The Enigmatic
1,4-Dioxane
1,4-Dioxane is a solvent used in products such as paints and lacquers and in processes such as organic chemical manufacturing. Previous extensive use of 1,4-dioxane with 1,1,1-trichloroethane (TCA) as a stabiliser and corrosion inhibitor means it is likely to be present at TCA-contaminated sites; however, technologies such as air stripping, that are effective for treating chlorinated solvents are often ineffective for treating dioxane. Due to the contaminant’s high solubility, low potential to partition from the dissolved phase to vapour, and low affinity for organic matter in soil, groundwater is the primary medium of concern for 1,4-dioxane. Among the most mobile organic contaminants in the saturated zone, it may be found farther downgradient than the leading edge of a solvent plume.
Likely to be
Carcinogenic to Humans

Classified by the United States Envrionmental Protection Agency (US EPA) as “likely to be carcinogenic to humans” by all routes of exposure, as of 2016, 1,4-dioxane had been identified at more than 34 sites on the US EPA National Priorities List (NPL), and may be present at many other sites where the common practice of analysing by a limited list of available methods for regulatory compliance has precluded its detection. 1,4-Dioxane is included on the US EPA’s fourth drinking-water Contaminant Candidate List (CCL4) and is included in the third Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR3). While a US federal maximum contaminant level (MCL) has not been established for 1,4-dioxane in drinking water, a lifetime Health Advisory (HA) of 0.2 mg/L has been established. In the United States, eighteen states have established drinking water and groundwater guidelines, ranging from 0.25 µg/L to 77 µg/L, with six states at or below 1 ppb.
Innovative Approach to
Proven Technology

Using a time-proven treatment approach in an innovative way, ECT2 designs ex situ water-treatment systems incorporating a carbonaceous synthetic adsorbent with a high affinity for 1,4-dioxane and other organic compounds. The product’s hydrophobic nature and unique pore size distribution facilitate the removal of 1,4-dioxane and other highly miscible organic contaminants from groundwater, enabling compliance with tight US permitting limits for 1,4-dioxane of less than 0.2 µg/L and delivering consistent, reliable treatment, independent of changes in influent concentrations, pH, and flow rates.
In Contrast to
GAC and AOP
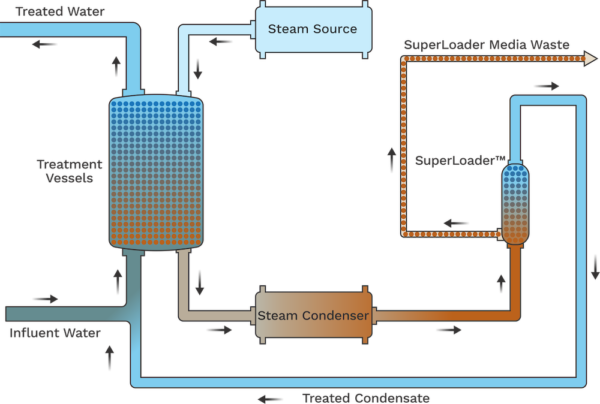
In contrast to GAC, which cannot reliably achieve stringent treatment requirements for 1,4-dioxane and must be reactivated off site, our synthetic adsorbent can be regenerated in place thousands of times using simple regenerative methods, such as low-pressure steam, with no loss of capacity or ability to achieve low-level effluent residuals. In addition, our technology does not experience the sensitivity to influent concentration and pH or the deleterious effects of free-radical scavenging and inorganic scale fouling that cause advanced oxidation processes (AOP) to struggle to achieve stable, consistent treatment results. Nor does it generate undesired reaction by-products, such as bromate, aldehydes, or organic acids, that may occur with the use of AOP. Our technology delivers results that meet stringent treatment requirements while simplifying process design, reducing long-term operating costs, increasing safety, and avoiding hazardous reagents and by-products.
Rapid-Deployment
Mobile Treatment System
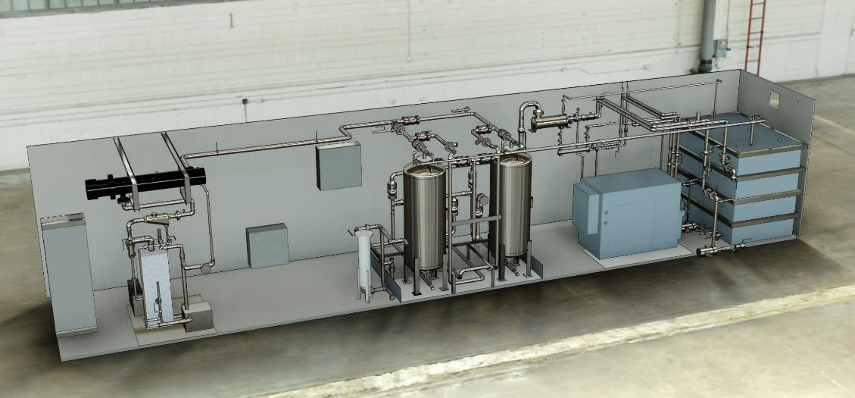
ECT2’s comprehensive process solution for 1,4-dioxane and specialty VOC contamination is available as a modular, portable system capable of rapid deployment and application as a source-area control measure. The M-25 mobile treatment system, with a nominal capacity of 1.6 litres per second (L/sec), is intended for sites needing immediate treatment for short- or long-duration assignments. System simplicity allows plug-and-play rapid installation, with limited operator oversight, and the system can be on site and ready for operation in as little as a few weeks. With in-place regeneration, the media can be reused thousands of times without losing its adsorption capacity or the ability to reliably achieve low-level effluent residuals.
Case Studies:
RAAF Base Tindal, NT Australia
Treatment Objective > (0.07 ug/L PFOS + PFHxS) (0.56 ug/L PFOA) Waste Generated 37m3 Volume Treated To Date >2.5 billion litres Treatment Outcome Achieved [...]
Content:
Sustainable PFAS Resin Technology Applied at Multiple Locations for Military Base Aquifer Remediation
Steve Woodard presented at RPIC 2019 the rapid deployment of a PFAS removal system for town water supply in Katherine, Australia.